Børstemark i stillehavsøsters - Dugnad for havet
Muddblemmer i stillehavsøsters. Foto: Lars Naustvoll, HI
Etter at Havforskningsinstituttet rapporterte de første observasjonene av «mudderblemmer» i stillehavsøsters har vi samarbeidet med eksperten Eivind Oug ved NIVA om å lage en beskrivelse av børstemarken Polydora websteri, arten som forårsaker mudderblemmer. Vi håper at både publikum og organisasjoner vil ta i bruk informasjonen og rapportere funn av mudderblemmer.
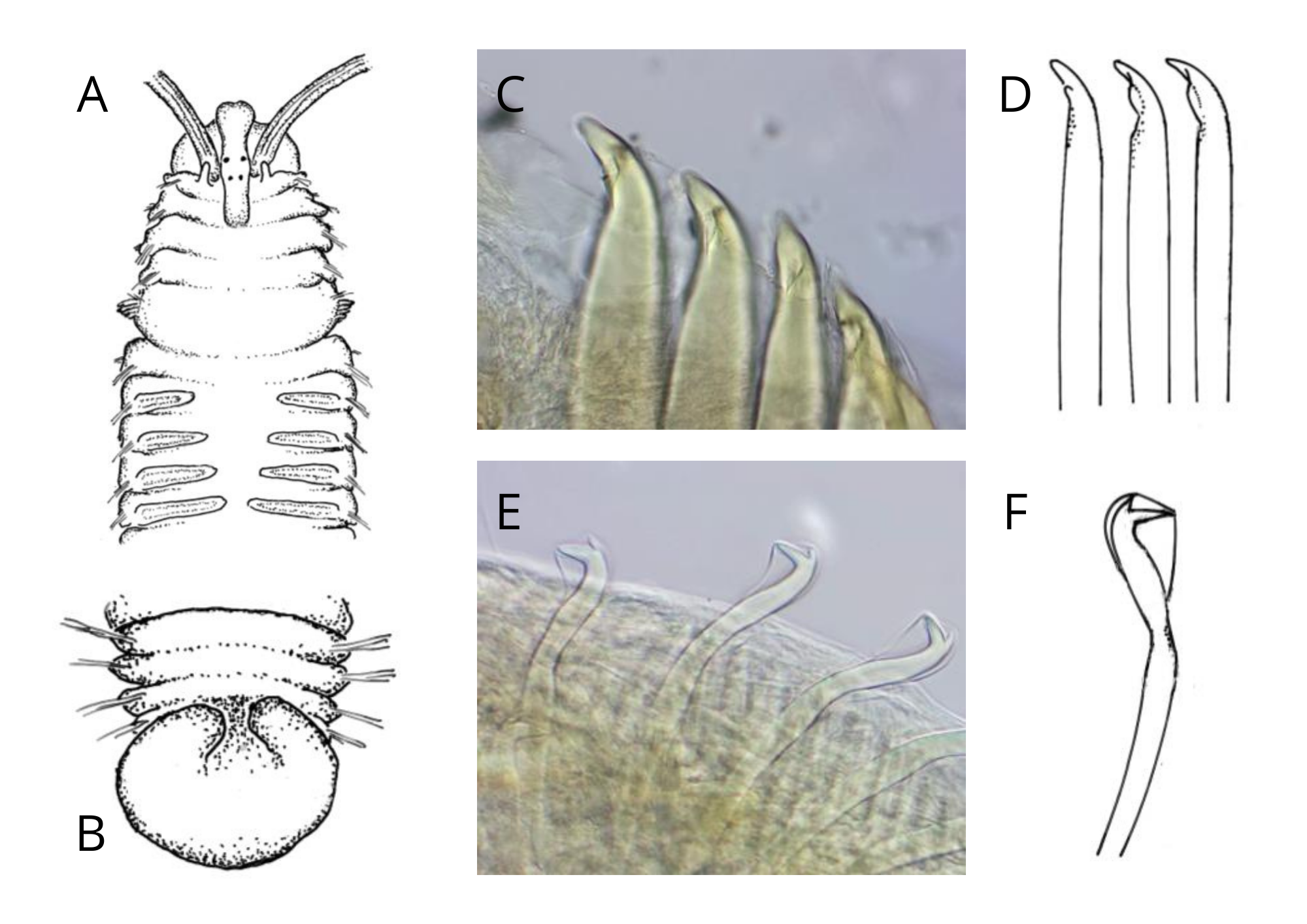
Kalkborende flerbørstemark Polydora websteri i stillehavsøsters
Polydora websteri er en kalkborende art av flerbørstemark som forårsaker en skallskade - såkalt mudderblemme (‘mud-blister’) - i skjell overstore deler av verden. Mudderblemme er en mørkfarget blæredannelse på skallets innside som dannes ved at marken borer seg gjennom skallet. Børstemarken, og avfallsprodukter,kapsles inn ved at skjellet produserer et tynt lag med kalk rundt fremmedelementet. Mudderblemmen vil over tid fylles med ekskrementer ogråtnende ufordøyd organisk materiale fra børstemarken. Mudderblemmer reduserer skjellets verdi til konsum og kan føre til dårligere vekst og kondisjon for skjellet.

Referanser
Blake, J.A. 1969. Reproduction and larval development of Polydora from northern New England (Polychaeta: Spionidae). Ophelia 7: 1-63.
Blake, J.A. 1971. Revision of the genus Polydora from the east coast of North America (Polychaeta: Spionidae). Smithsonian contributions to zoology 75: 1-32.
Martinelli J.C., Lopez, H.M et al. 2020. Confirmation of the shell-boring oyster parasite Polydora websteri (Polychaeta: Spionidae) in Washington State, USA. Scientific Reports 10:3961 (2020).
Radashevsky, V.I. 1999. Description of the proposed lectotype for Polydora websteri Hartman in Loosanoff & Engle, 1943. Ophelia 51: 107- 113.
Radashevsky, V.I., Pankova, V.V. 2006. the morphology of two sibling sympatric Polydora species (Polychaeta: Spionidae) from Sea of Japan. Journal Marine Biology Association UK 86: 245-252.
Read, G.B. 2010. Comparison and history of Polydora websteri and P. haswelli (Polychaeta: Spionidae) as mud-blister worms in New Zealand shellfish. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 44: 83-100.
Sato-Okoshi, W., Abe, H. 2013. Morphology and molecular analysis of the 18S rRNA gene of oyster shell borers, Polydora species (Polychaeta: Spionidae), from Japan and Australia. J. Mar. Biol. Ass UK 93: 1279-1286.
Simon, C.A., Sato-Okoshi W. 2015. Polydorid polychaetes on farmed moluscs: distribution, spread and foctors contributing to their success. Aquaculture Environmental Interactions 7: 147-166.
Spencer, L.H.., Martinelli, J.C., King, T.L. et al. 2021. The risks of shell-boring polychaetes to shellfish aquaculture in Washington, USA: a mini-review to inform mitigation actions. Aquaculture Research 52: 438-455.
Waser, A.M., Lackschewitz, D., Knol, J., Reise, K., Wegner, K.M., Thieltges, D.W. 2020. Spread of the invasive shell-boring annelid Polydora websteri (Polychaeta, Spionidae) into naturalised oyster reefs in the European Wadden Sea. Marine Biodiversity 50: 63 (2020)
Ye, L., Cao, C., Tang, B., Yao, T., Wang, R., Wang, J. 2017. Morphological and molecular characterization of Polydora websteri (Annelida: Spionidae), with remarks on relationship of adult worms and larvae using mitochondrial COI gene as a molecular marker. Pakistan Journal of Zoology 49: 699-710
Publisert: 09.06.2022 Oppdatert: 31.07.2024