Examples of Research projects delivering data directly to the regulatory authorities
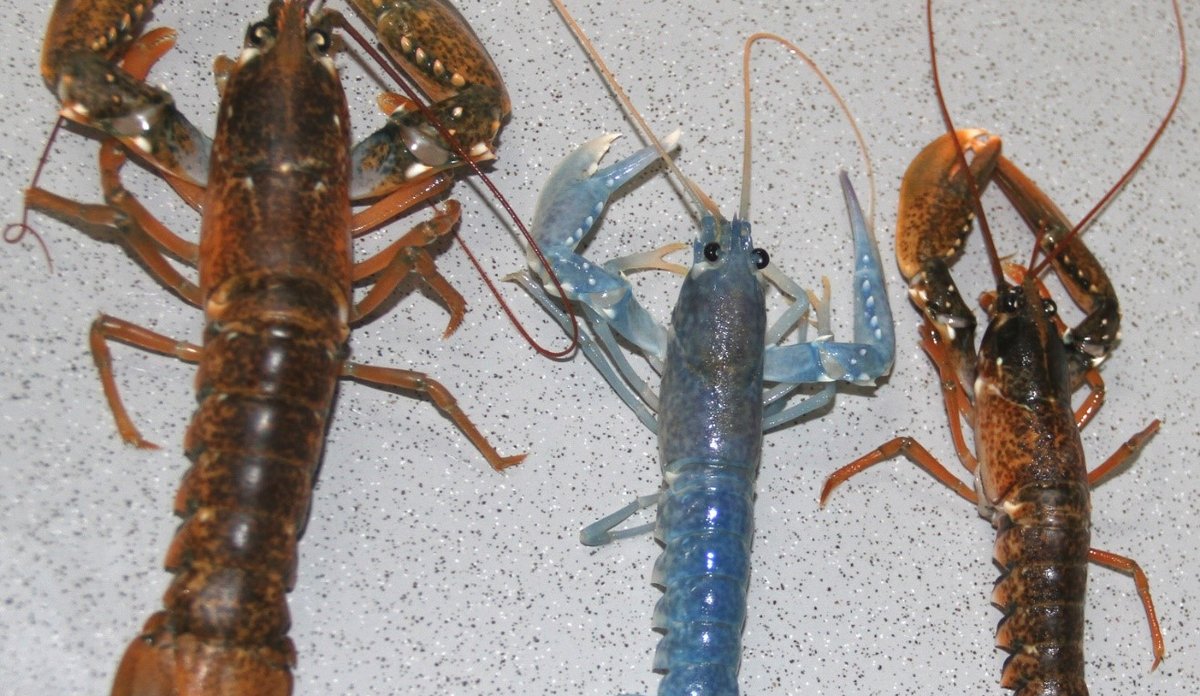

Our laboratory provides routine identification of American lobsters and hybrids captured in European waters.
Photo: Eva Farestveit“Real time” genetic management of marine fisheries
Starting in 2007 in Lofoten, and 2009 in Borgundfjord, the Pantophysin gene, commonly known as PanI, has been used to estimate the frequency of Northeast Arctic cod (NEAC) and Norwegian coastal cod (NCC) in the Atlantic’s first “real-time” genetic monitoring program. Both these monitoring programs have been in operation yearly until today’s date, and have supplied the Norwegian Directorate of Fisheries, who are responsible for regulation and inspection of marine fisheries in Norway, with weekly estimates of NEAC and NCC fractions. The overall aims of these programs have been to protect the dwindling NCC resource from over-exploitation by the commercial fishing fleet, while simultaneously providing a good management regime for exploitation of the sustainable NEAC. These unique data sets, which collectively include the genetic profile of ~25 000 cod have also given us unprecedented insights into the relationships between NEAC and NCC. All of these works are published 58,137.
The genus Sebastes or redfish is composed of at three species in Norwegian waters. Sebastes mentella and S. norvegicus are the commercial important species. These two species can be difficult to differentiate by morphology, and particularly as juveniles 62,64. In a large program, based on DNA markers we are identifying redfish juveniles in bycatches from fisheries for northern shrimps. If the estimated fraction of S. norvegicus are high the fishery will be closed.
Genetic support for identification and modification of stock boundaries used in fisheries management
Data from our population genetic and genomic studies (above) are typically included either directly or indirectly in the management regimes of the species under investigation. I.e., genetic data are used together with other fisheries data to help delineate the management units. A good example of this is the modification of the ICES-recommended European sprat management units in the NE Atlantic 104 – see figure below. In addition, data from both corkwing wrasse 82 and ballan wrasse 79 have showed a deep evolutionary divide across the sandy beaches region of Jæren – demonstrating that transition of cleaner fish from southern to mid-Norway regions will lead to mixing fish from phylogenetically highly distinct units and thus represents dubious practice – as observed by detection of aquaculture translocated escapees and potentially hybrids in Mid-Norway 83. Until recently, Norwegian coastal cod was managed as two stocks at 62°. However, based partially upon genetic data from the group 53,54, this resource is now managed in three separate stocks and our future recommendation will include further divisions. Many of the other examples of population genetics and geonomics studies above have also contributed to revisions of fishery management regimes.
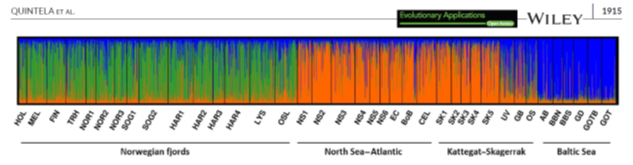
Structure plot depicting genetic relationships among samples of sprat in the NE Atlantic. Norwegian fjords are clearly genetically distinct from North Sea-Atlantic sprat as well as the Baltic. In the inner-part of Kattegat there is a transition zone identified by samples UV GB and OS being a genetic mixture of Baltic and North Sea-Atlantic sprat. These results modified ICES management boundaries immediately 104.
Salmon genetic baselines
Norway has >400 rivers supporting Atlantic salmon populations. Through a variety of National, internal and EU-funded projects (e.g., SALEA-Merge 2008-2011), we have established a genetic baseline of Norwegian salmon populations in >150 of these rivers 97. These data have been mixed with international data sets to enable assignment of post-smolt and adult salmon caught in oceanic cruises and fisheries back to the regions of origin 138. This allows for mapping of migration routes and oceanic feeding areas for salmon from different regions, and better understanding of the differences observed in marine mortality and growth over time, and between regions, a focus area for the NRC project SeaSalar where IMR and the research group is a main partner. The genetic baseline was recently applied to describe the distribution of 9000+ Atlantic salmon post smolts caught in the North Atlantic over the last decades 139.
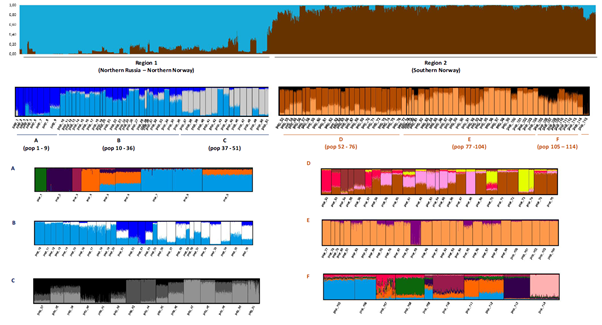
From Wennevik et al., 97. Genetic structure of 115 Norwegian salmon populations – illustrating large among and within region differences.
A more detailed baseline, both in terms of population coverage and number of genetic markers mapped, was developed for the northern populations of Atlantic salmon from northern Norway and Russia in the EU-funded project Kolarctic-salmon. The baseline developed here was applied for investigating exploitation patterns of coastal fisheries for salmon in northern Norway. The project provided detailed information on where and when different salmon populations are exploited in marine fisheries. The results have been implemented in the management regime for coastal fisheries for these northern populations 140.

Photo: Kevin Glover
The minke whale DNA register
Each year Norway carries out a commercial harvest of minke whales in the Northeast Atlantic. As a part of this highly regulated harvest regime, tissue samples are taken from all captured whales and their individual DNA profile is entered in a DNA register 141. These DNA profiles follow meat being exported to Japan, and permit control over the domestic market. The register includes the DNA profiles and biological information for ~10 000 minke whales and has provided us with unique insights into this species and its connectivity with its close relatives. For example, we have detected Antarctic minke whales in the Arctic 142, identified fertile hybrids between these species thought to have been isolated for millions of years 111,143, identified Greenland sharks feeding on offal from whaling operations 144, and identified the number of putative populations present in the Management Areas 102. The DNA register is in operation every year, and data from the genomic work has been made openly accessible so that researchers in all regions of the world can identify potential minke whale hybrids and long-distance migrants against our data 111.
Genetic identification of invasive American lobsters in Europe
The group has a long history of working on the European lobster, ranging from population genetic structure, aquaculture production, sea ranching, MPAs and identification of American lobsters 108-110,115,145,146. Concerns about the presence of American lobster on the European continent has been reported from Great Britain, Ireland, Norway, Denmark and Sweden. Since 2000, about 60 lobsters have been genetically identified by IMR as American lobsters, 29 in Norwegian waters. In 2015, IMR identified three American lobsters found in Ireland, three in Sweden and three in Norway. In 2010, the first crossbreeding between American and European lobster was found in Norway, one more in 2014 in Sweden, and again in Norway in 2015. The ecological and environmental risks associated with American lobster are primarily introducing new diseases and parasites, but hybridization with the European lobster, rapid geographic spreading through pelagic larval stages, as well as competition with native lobsters are also of great concern, especially with the identification of hybrids. We are now investigating if these hybrids are fertile.
Forensic identification of farmed escapees with DNA
The group has played a pioneering role in developing and implementing DNA methods to trace unreported escapes back to their farms of origin. The work was initiated in the mid-2000s, and quickly resulted in the world's first example of using DNA to trace escapees back to their farms of origin 147. This case ended up in a fine for the company found in breach of regulations. This marked the start of extensive work to develop the DNA tracing method further 148, including the ability to trace farmed escaped rainbow trout 149 and Atlantic cod 48,150. The method has been applied in ~20 cases for the regulatory authorities in the period 2007-todays date 148, and has involved a diverse set of cases investigated 151,152. This work is still run as a routine service for the Norwegian Directorate of Fisheries who are the responsible authority for aquaculture regulation in Norway.

Photo: Kevin Glover
The National Monitoring Program for incidence of farmed escaped salmon in >200 rivers annually
The incidence of farmed escaped salmon in Norwegian rivers has been monitored since the late 1980s. However, in 2014, the Norwegian government instructed the Institute of Marine Research to establish a new and nationally-coordinated monitoring program for farmed escapees. This involved starting a project group consisting of >20 researchers from five Norwegian research institutes and establishing a coordinated sampling and reporting program. Based upon estimates originating from summer angling surveys, dedicated autumn angling surveys, fish traps and snorkeling-surveys, the incidence of farmed escapees is now estimated in >200 Norwegian rivers annually 30and has been published in a scientific paper 31. Validation of some of the methology has also been published 153. Data from this program feed into the Institute of Marine Research’s risk assessment (below), as well as providing the basis for the national mitigation strategy to remove farmed escapees from the spawning grounds in order to reduce the potential for genetic interactions.
The report from the monitoring program itself is available here.
The annual “Risk Assessment of Norwegian Aquaculture”
Since 2011, the Institute of Marine Research has published a yearly risk-assessment of Norwegian aquaculture 154. Farmed escapees and genetic interactions with wild conspecifics is ranked as the second largest challenge to an environmentally sustainable aquaculture industry and the research group is responsible for assessing the risk related to farmed escapee from salmon aquaculture, which includes a report of the risk assessment of further genetic introgression of escaped salmon to wild populations, as well as a report documenting the knowledge status of this research area. These documents are, among other things, used by the Norwegian government to regulate the aquaculture industry. Part of this work has also been published scientifically 32.
The Risk Assessment report is available here.
Scientific contributions to the EAF-Nansen programme
One of the main research areas identified in the EAF-Nansen Programme 2017–2021 science plan, was dealing with the impacts of fishing. The Population genetics group has been responsible for stock identity, for both pelagic and demersal species. One of the other key elements in the Nansen program is transfer of knowledge and all work is done in cooperation with African partners. The Population Genetics group has identified new genetic markers for various species of interest in the programme and several studies on economically important pelagic species (Sardinella aurita and Scomber colias) have been produced in collaboration with our African partners. There has also been a training element with associated transfer of knowledge from IMR to the partners.
References: Key publications from the IMR Population Genetics group.pdf
Published: 03.03.2022

